Ransomware
What is Ransomware?

Ransomware is a form of malware that encrypts a victim's data or locks them out of their computer systems. The attacker then demands a ransom payment, often in cryptocurrency, in exchange for restoring access to the data or system. SMEs are often seen as easy targets by cyber criminals hoping to make some easy money through the use of ransomware for a variety of reasons such as:
Limited Budgets
Many SMEs cannot afford robust cybersecurity measures like managed security services or advanced endpoint protection.
Lack of Expertise
SMEs often do not have dedicated IT staff or cybersecurity professionals, leaving them less prepared to respond to threats.
Over-Reliance on Technology
Many SMEs increasingly rely on digital tools but do not adequately secure these systems.
Human Error
Employees in SMEs may lack training on recognizing phishing emails or avoiding malicious downloads, which are common ransomware delivery methods.
How Ransomware Works
- Infection: Ransomware often spreads through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or infected websites. Clicking on a malicious link or file can initiate the ransomware attack.
- Encryption or Lockout: Once installed, ransomware encrypts files on the victim's system or locks them out of their device. Encrypted files are unusable without a unique decryption key held by the attacker.
- Ransom Demand: A message appears, often with instructions for payment in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Sometimes, a countdown timer increases the urgency, threatening to delete data if the ransom isn’t paid.
- 4. Payment & Consequences: Paying the ransom doesn’t guarantee the victim will regain access. Attackers may provide a decryption key, but some victims are never helped even after paying.
How Ransomware Impacts Business
Financial Impact
Ransomware imposes significant financial burdens on SMEs, as they may feel compelled to pay ransoms due to the critical nature of their data and limited recovery options. These payments can range from thousands to millions of dollars. Additionally, the operational downtime caused by encrypted systems leaves businesses unable to function, resulting in lost revenue and reduced productivity. Recovery costs further strain budgets, as SMEs must invest in IT support, forensic analysis, and new security measures to restore operations.
Reputational Damage
The reputational harm from ransomware attacks can be profound for SMEs. If sensitive customer data is exposed, the resulting loss of trust can severely impact customer retention and loyalty. Negative publicity surrounding the attack can amplify the damage, undermining the SME’s brand and deterring potential customers and business partners.
Operational Disruption
Ransomware disrupts critical operations by encrypting key business systems, such as financial records and customer relationship management tools, bringing productivity to a halt. This operational paralysis can have broader implications, as disruptions to an SME’s activities may extend to its supply chain, damaging relationships with partners and clients who depend on their services.
Legal and Regulatory Consequences
Ransomware attacks can expose SMEs to serious legal and regulatory repercussions. Many SMEs handle sensitive data that must comply with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, and a breach can result in fines, legal action, and regulatory scrutiny. Additionally, businesses are often required to notify affected parties of data breaches, leading to further financial and reputational costs.
Increased Vulnerability
Ransomware attacks often leave SMEs more vulnerable to future incidents. Paying a ransom or failing to address underlying weaknesses can attract repeat attacks, as cybercriminals view such businesses as easy targets. With limited cybersecurity measures, such as endpoint protection, regular updates, and employee training, SMEs remain particularly susceptible to exploitation.
How to Defend Against Ransomware Attacks
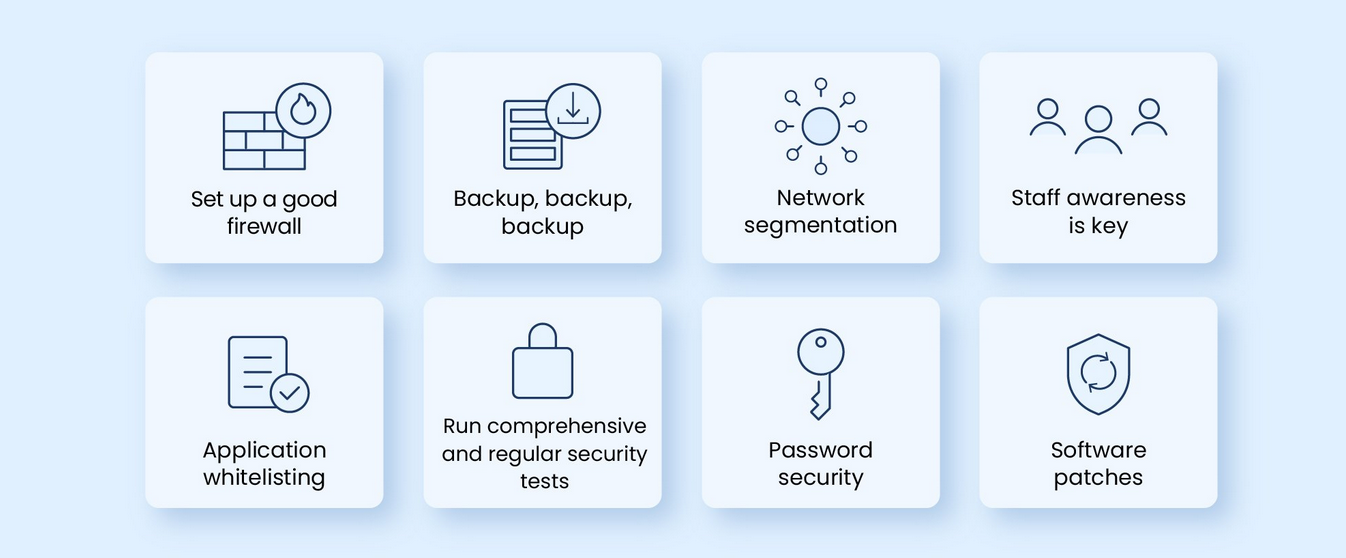
Regular Backups
SMEs can reduce the impact of ransomware attacks by maintaining regular backups of critical data. These backups should be stored offline or in secure, isolated environments to prevent attackers from accessing them. Regularly testing these backups ensures that data can be restored quickly and reliably in case of an attack.
Training and Awareness
Since phishing emails and malicious links are common ransomware delivery methods, educating employees is critical. SMEs should implement regular cybersecurity training to help staff recognize phishing attempts, avoid suspicious downloads, and practice safe online behavior. Encouraging a culture of vigilance reduces the likelihood of human error leading to an attack.
Endpoint and Network Security
Deploying robust endpoint protection software and firewalls is essential for SMEs to defend against ransomware. These tools can detect and block malicious files or activities before they compromise systems. Network segmentation also helps limit the spread of ransomware by isolating infected systems from the rest of the network.
Software Updates and Patching
Keeping all software, operating systems, and applications up to date is a critical defense against ransomware. Attackers often exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software. By applying patches promptly, SMEs can close these security gaps and reduce the risk of being targeted.
Access Control and Privilege Management
Limiting user access to sensitive systems and data minimizes the damage ransomware can inflict. SMEs should adopt a principle of least privilege, granting employees access only to the resources they need for their roles. Multifactor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security, making it harder for attackers to breach accounts.
Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined and tested incident response plan prepares SMEs to act swiftly in the event of a ransomware attack. This plan should outline steps to isolate infected systems, communicate with stakeholders, and restore operations from backups. A prepared team can minimize downtime and financial losses.
Email Filtering and Anti-Phishing Tools
Implementing email filtering solutions can help SMEs detect and block phishing attempts, a primary vector for ransomware attacks. Advanced anti-phishing tools use machine learning to identify suspicious emails and attachments, reducing the chances of an employee falling victim.
Cybersecurity Insurance
Obtaining cybersecurity insurance can help SMEs manage the financial fallout of a ransomware attack. Policies often cover costs related to recovery, legal fees, and customer notifications. While it doesn’t prevent attacks, insurance can provide critical financial support during recovery.
Threat Monitoring
Deploying advanced monitoring tools to detect and respond to suspicious activities in real-time is a proactive way for SMEs to guard against ransomware. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) can help identify and block potential threats before they cause harm.
Ransomware is a serious and growing threat to SMEs and the consequences of an attack can be devastating, potentially jeopardizing the survival of a small business. However, by understanding how ransomware works and adopting proactive measures, SMEs can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to attacks. Regular backups, employee training, robust security systems, and a comprehensive incident response plan are crucial components of a strong defense. Investing in tools such as email filtering, threat monitoring, and cybersecurity insurance can help SMEs prepare for and mitigate the effects of an attack.